MCP安全应用和问题
MCP安全应用和问题
MCP 相关安全项目
- MCP 安全检查清单:AI 工具生态系统安全指南
MCP-Security-Checklist/README_CN.md at main · slowmist/MCP-Security-Checklist
一些安全类 MCP 使用
IDA-Pro-MCP
:::info 我这里走的 stdio 方案
:::
项目地址
GitHub - mrexodia/ida-pro-mcp: MCP Server for IDA Pro.
先安装好 uv,(类似 pip)
pip uninstall ida-pro-mcppip install git+https://github.com/mrexodia/ida-pro-mcp
ida-pro-mcp --install进入 IDA 打开文件,这里得把这个服务给起起来
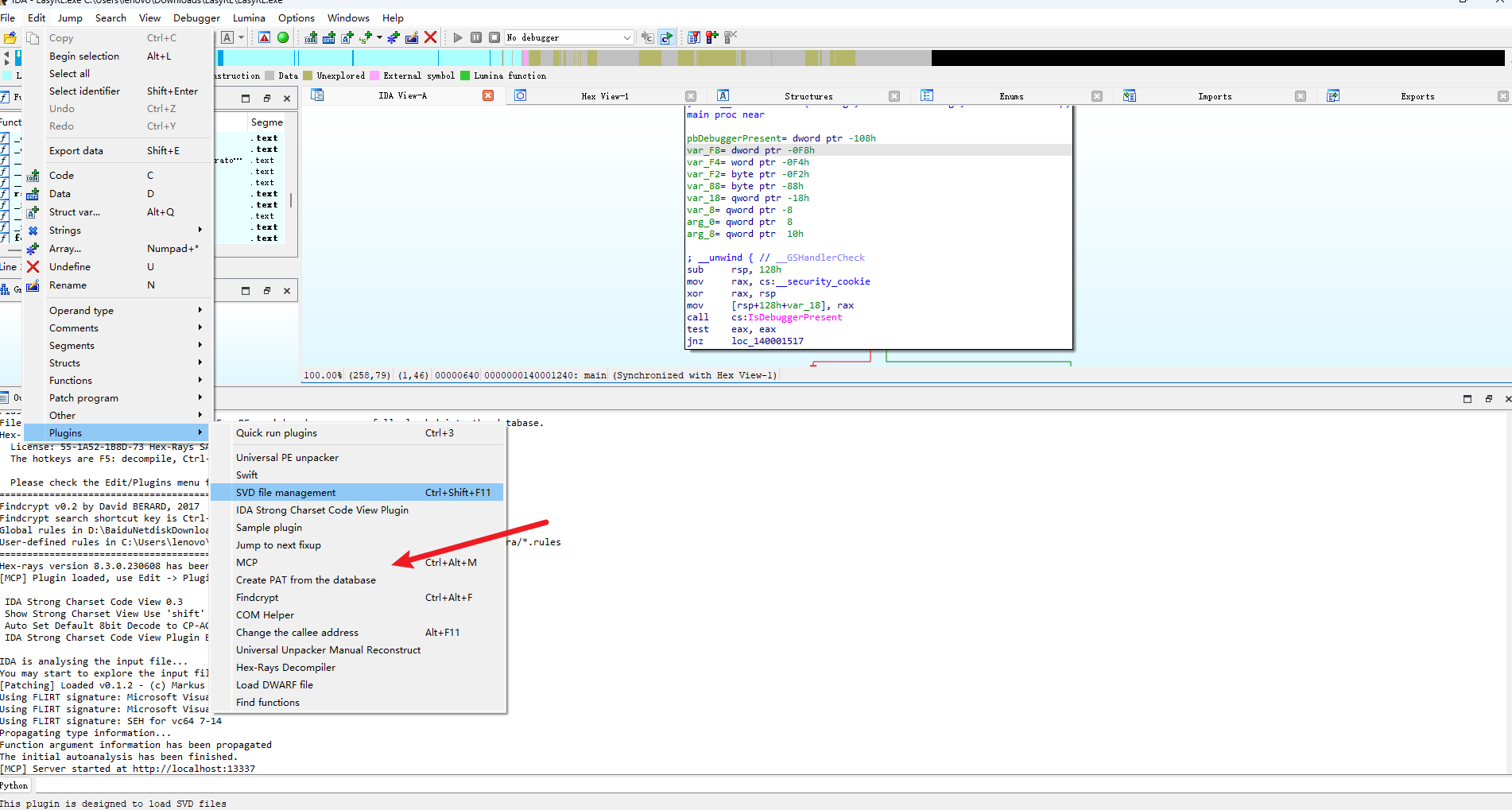
MCP 客户端配置如下
{ "mcpServers": { "IDA Pro MCP": { "command": "uv", "args": ["run", "ida-pro-mcp", "--install-plugin"], "timeout": 1800 } }}用 cursor 或者 trae 这些,这里演示一下 trae
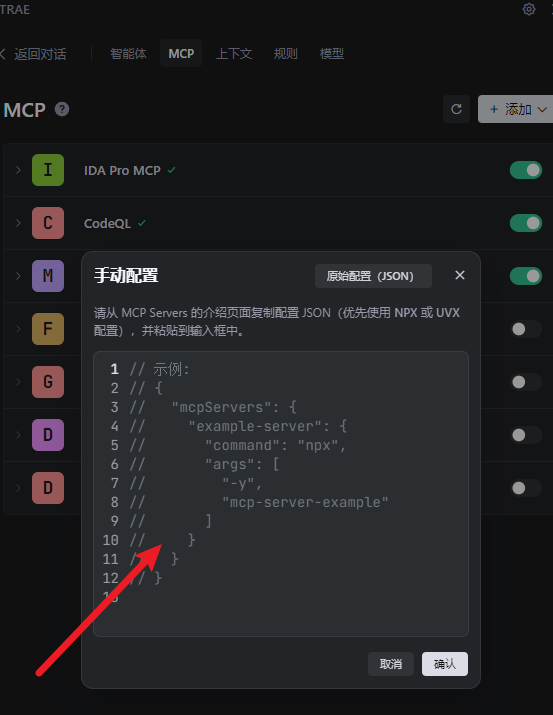
Trae 配置
可以新建一个智能体专门搞这个 ida 的
这里你提示词很重要
专注于 CTF 比赛的,可以再改改啥的
具体效果
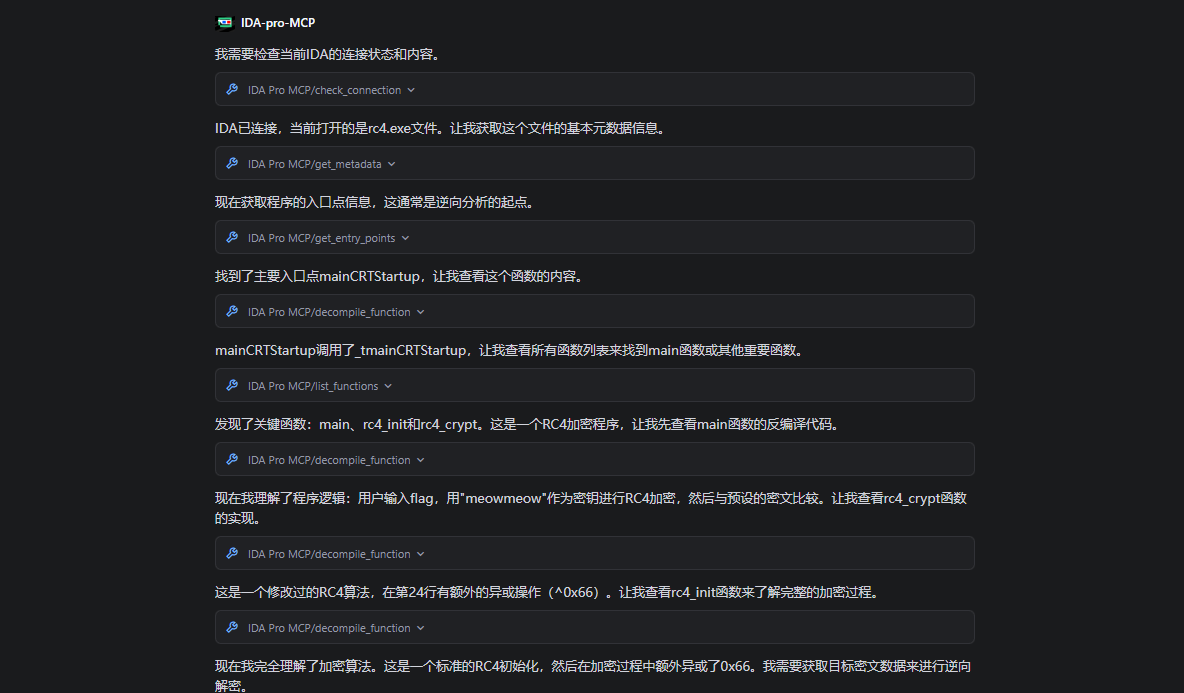
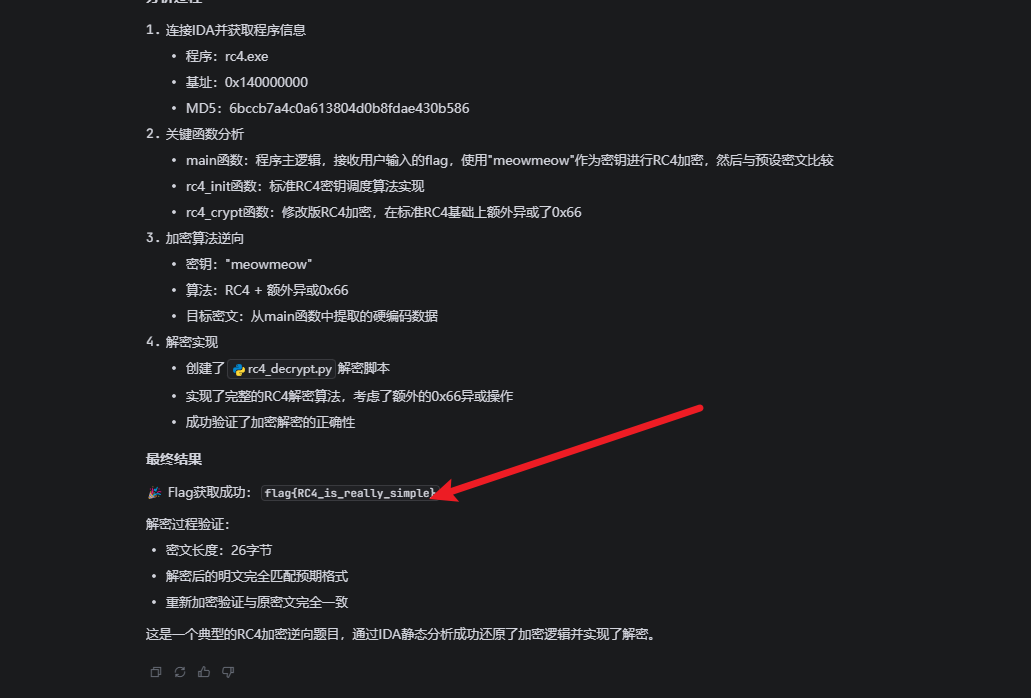
具体脚本
#!/usr/bin/env python3# RC4 解密脚本# 基于IDA分析的rc4.exe程序
def rc4_init(key): """RC4密钥调度算法""" S = list(range(256)) j = 0 key_len = len(key)
for i in range(256): j = (j + S[i] + key[i % key_len]) % 256 S[i], S[j] = S[j], S[i]
return S
def rc4_decrypt(ciphertext, key): """RC4解密函数(考虑额外的0x66异或)""" S = rc4_init(key) i = j = 0 plaintext = []
for byte in ciphertext: i = (i + 1) % 256 j = (j + S[i]) % 256 S[i], S[j] = S[j], S[i]
# 先去除额外的0x66异或,再进行RC4解密 decrypted_byte = (byte ^ 0x66) ^ S[(S[i] + S[j]) % 256] plaintext.append(decrypted_byte)
return bytes(plaintext)
def main(): # 从IDA分析得到的密文数据(v6数组的值) # v6[0] = 0xF225450DA959419D # v6[1] = 0x424C79FD1B3DA063 # v6[2] = 0x77255DEA8E102BEC # v7 = 457 (0x01C9)
# 将64位整数转换为字节数组(小端序) ciphertext = []
# v6[0] val1 = 0xF225450DA959419D ciphertext.extend([(val1 >> (8*i)) & 0xFF for i in range(8)])
# v6[1] val2 = 0x424C79FD1B3DA063 ciphertext.extend([(val2 >> (8*i)) & 0xFF for i in range(8)])
# v6[2] val3 = 0x77255DEA8E102BEC ciphertext.extend([(val3 >> (8*i)) & 0xFF for i in range(8)])
# v7 = 457 val4 = 457 ciphertext.extend([(val4 >> (8*i)) & 0xFF for i in range(2)])
print(f"密文长度: {len(ciphertext)}") print(f"密文 (hex): {' '.join(f'{b:02x}' for b in ciphertext)}")
# RC4密钥 key = b"meowmeow" print(f"密钥: {key.decode()}")
# 解密 plaintext = rc4_decrypt(ciphertext, key)
print(f"明文 (hex): {' '.join(f'{b:02x}' for b in plaintext)}") print(f"明文 (ascii): {plaintext.decode('ascii', errors='ignore')}")
# 验证:重新加密看是否匹配 print("\n=== 验证 ===") test_encrypt = rc4_encrypt(plaintext, key) print(f"重新加密: {' '.join(f'{b:02x}' for b in test_encrypt)}") print(f"原始密文: {' '.join(f'{b:02x}' for b in ciphertext)}") print(f"匹配: {test_encrypt == ciphertext}")
def rc4_encrypt(plaintext, key): """RC4加密函数(包含额外的0x66异或)""" S = rc4_init(key) i = j = 0 ciphertext = []
for byte in plaintext: i = (i + 1) % 256 j = (j + S[i]) % 256 S[i], S[j] = S[j], S[i]
# 先进行RC4加密,再异或0x66 encrypted_byte = (byte ^ S[(S[i] + S[j]) % 256]) ^ 0x66 ciphertext.append(encrypted_byte)
return ciphertext
if __name__ == "__main__": main()具体响应如下
密文长度: 26密文 (hex): 9d 41 59 a9 0d 45 25 f2 63 a0 3d 1b fd 79 4c 42 ec 2b 10 8e ea 5d 25 77 c9 01密钥: meowmeow明文 (hex): 66 6c 61 67 7b 52 43 34 5f 69 73 5f 72 65 61 6c 6c 79 5f 73 69 6d 70 6c 65 7d明文 (ascii): flag{RC4_is_really_simple}
=== 验证 ===重新加密: 9d 41 59 a9 0d 45 25 f2 63 a0 3d 1b fd 79 4c 42 ec 2b 10 8e ea 5d 25 77 c9 01原始密文: 9d 41 59 a9 0d 45 25 f2 63 a0 3d 1b fd 79 4c 42 ec 2b 10 8e ea 5d 25 77 c9 01匹配: TrueIDA-mcp 具体工具列表
| 类别 | 工具名称 |
|---|---|
| 连接测试 | check_connection |
| 元数据 | get_metadata |
| 函数查找 | get_function_by_name, get_function_by_address |
| 当前定位 | get_current_function, get_current_address |
| 列出函数 | list_functions |
| 字符串处理 | list_strings, search_strings |
| 入口点 | get_entry_points |
| 反编译 | decompile_function |
| 反汇编 | disassemble_function |
| 交叉引用 | get_xrefs_to |
| 注释 | set_comment |
| 变量/函数重命名 | rename_local_variable, rename_global_variable, rename_function |
| 设置类型 | set_global_variable_type, set_local_variable_type, set_function_prototype, declare_c_type |
| 数字转换 | convert_number |
CloudSword-MCP(云鉴)
项目地址
GitHub - wgpsec/cloudsword: 一款帮助云租户发现和测试云上风险、增强云上防护能力的综合性开源工具
:::info 我们这里只讨论使用 MCP 的案例和效果,不去探究工具本身使用
但是实际测试情况这个 MCP 做的不够好,还是没有很完整
:::
- SSE 配置
启动 sse
./cloudsword sse http://localhost:8080- STDIN 配置如下
command 中设置你的软件位置
{ "mcpServers": { "cloudsword": { "isActive": true, "name": "cloudsword-MCP", "description": "Cloudsword 安全分析服务", "type": "stdio", "command": "E:\\Tools\\利用工具\\云\\cloudsword_v0.0.2_windows_amd64\\cloudsword.exe", "args": [ "stdio" ], } }}为了更好地发挥工具 MCP 效果,需要一些比较合适的提示词
可用提示词
你现在是我的云安全助手,集成了 CloudSword 模块。你的目标是:帮助我在多云环境下快速发现资产、分析风险、执行安全操作。
使用规则:1. 当我提出问题时,请自动选择最合适的 CloudSword 模块并运行,并返回结果。2. 在调用前,优先检查需要的认证参数(如 ACCESS_KEY_ID / ACCESS_KEY_SECRET 等),如果缺失请明确提示我设置。3. 若有多个模块都可能符合要求,请优先选择推荐评级更高的模块。4. 输出时,请用清晰的表格或列表展示结果,不要只给原始 JSON。5. 如果模块运行失败,请输出报错信息,并提示我可能的修复办法。6. 如果我提出的问题不在现有模块范围,请告诉我该模块暂不支持,并给出可选的替代方案。
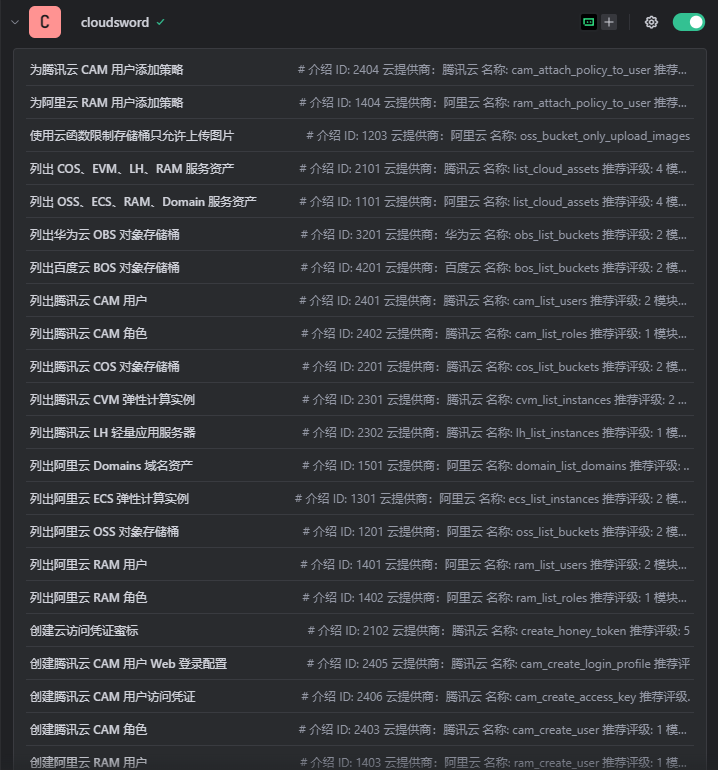
常见问题示例:- “列出阿里云 OSS 存储桶” → 调用 oss_list_buckets- “搜索阿里云 OSS 对象” → 调用 oss_search_objects- “列出阿里云 ECS 实例” → 调用 ecs_list_instances- “查看阿里云 RAM 用户” → 调用 ram_list_users- “列出腾讯云 COS 存储桶” → 调用 cos_list_buckets- “查看腾讯云 CVM 实例列表” → 调用 cvm_list_instances- “查看腾讯云 CAM 用户” → 调用 cam_list_users- “列出华为云 OBS 存储桶” → 调用 obs_list_buckets- “列出百度云 BOS 存储桶” → 调用 bos_list_buckets- “列出七牛云 KODO 存储桶” → 调用 kodo_list_buckets- “生成腾讯云蜜罐凭证” → 调用 create_honey_token
注意:- 默认使用环境变量中的云访问密钥进行认证。- 在输出中,敏感信息(如 AccessKey)不要直接暴露。- 仅执行只读和合法的安全分析操作,不进行破坏性命令。具体测试
配置之后可以看下工具列表
使用示例
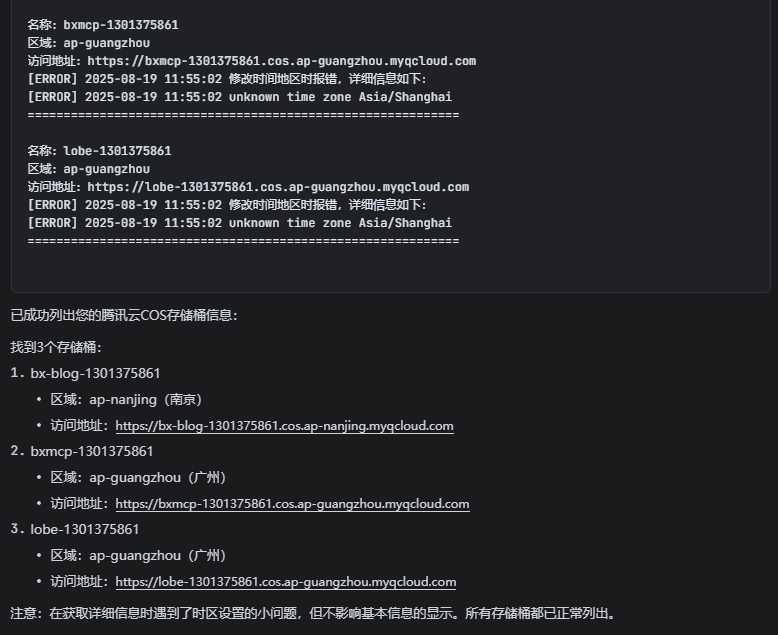
Q:列出腾讯云用户的 COS 储存桶
A:响应如下,调用查看了我的一些储存桶
查看 MCP 信息
MCP 协议核心是 3 大类:
- Tools:动作(可调用函数)。
- Prompts:提示模板。
- Resources:数据源。
再加上 notifications(动态更新)和 capabilities(初始化声明)。
这里具体如下,
信息列表
让 AI 总结一下
🛠 Tools(工具)
- 就是你已经用过的
tools/list、tools/call。 - 描述的是“可以被调用的函数/动作”。
- 每个 tool 有
name、description、inputSchema(参数 JSON Schema),调用结果可能包含text/data/messages。
📑 Prompts(提示模版)
- MCP 支持列出一组可用的 提示词模板,由服务端定义。
- 客户端可以
prompts/list→ 选择一个模板,再prompts/get→ 填充参数,得到完整的 prompt。 - 用途:比如一个服务端提供“代码解释”、“安全检查”等预设提示,让客户端直接拿来喂 LLM。
📂 Resources(资源)
- MCP 可以暴露一组 外部资源,比如文件系统、数据库、HTTP API。
- 客户端通过
resources/list看有哪些资源(每个资源有 URI、mimeType、描述)。 - 再用
resources/read(或 watch API)获取内容。 - 用途:文件浏览、项目上下文加载、数据库表结构、日志流……
🔔 Notifications(事件通知)
- 服务器可以主动发事件,比如:
notifications/tools/list_changed→ 提示工具列表更新notifications/resources/updated→ 某个资源内容变化
- 这样客户端就能动态刷新,而不是死板地只用启动时的能力。
🧩 Capabilities(能力声明)
- 在
initialize返回里,服务端会告诉客户端“我支持哪些模块”:tools?prompts?resources?logging?/experimental?
使用官方 mcp SDK
具体 uv 安装如下
# 安装uv pip install "mcp[cli]"
# 运行uv run python your_script.py具体操作如下
import asynciofrom mcp import ClientSession, StdioServerParametersfrom mcp.client.stdio import stdio_client
CLOUDSWORD = r"E:\Tools\利用工具\云\cloudsword_v0.0.2_windows_amd64\cloudsword.exe"
async def main(): server = StdioServerParameters( command=CLOUDSWORD, args=["stdio"], ) async with stdio_client(server) as (read, write): async with ClientSession(read, write) as session: # 初始化握手 await session.initialize() # 拉取工具列表 resp = await session.list_tools() print("== Available tools ==") for tool in resp.tools: print(f"- {tool.name}: {tool.description or ''}") if tool.inputSchema: print(f" schema: {tool.inputSchema}\n")
if __name__ == "__main__": asyncio.run(main())使用 FastMCP
具体环境采用
uv pip install fastmcp具体操作如下
import asynciofrom fastmcp import Clientfrom fastmcp.client.transports import StdioTransport
CLOUDSWORD = r"E:\Tools\利用工具\云\cloudsword_v0.0.2_windows_amd64\cloudsword.exe"
async def main(): transport = StdioTransport(command=CLOUDSWORD, args=["stdio"]) async with Client(transport=transport) as client: tools = await client.list_tools() for t in tools: print(f"- {t.name}: {t.description}")
if __name__ == "__main__": asyncio.run(main())